Salt and High Blood Pressure: Myth or Truth?
Salt is an age-long staple to diets and has various uses, from preserving food to adding flavor to meals. With how nutrition has evolved over the years, your viewpoint on how its consumption affects health must be well-informed.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common medical condition that may lead to serious health problems left untreated. The relationship between salt and high blood pressure is one topic with misconceptions and arguments in food and wellness.
In this article, we will consider high blood pressure, the role of salt in the human body, and the link between salt consumption and blood pressure. We will also debunk myths about their relationship, examine other contributing factors, explore healthier alternatives for salt, and offer practical recommendations for managing your blood pressure through dietary changes.
Understanding High Blood Pressure
What is Blood Pressure?
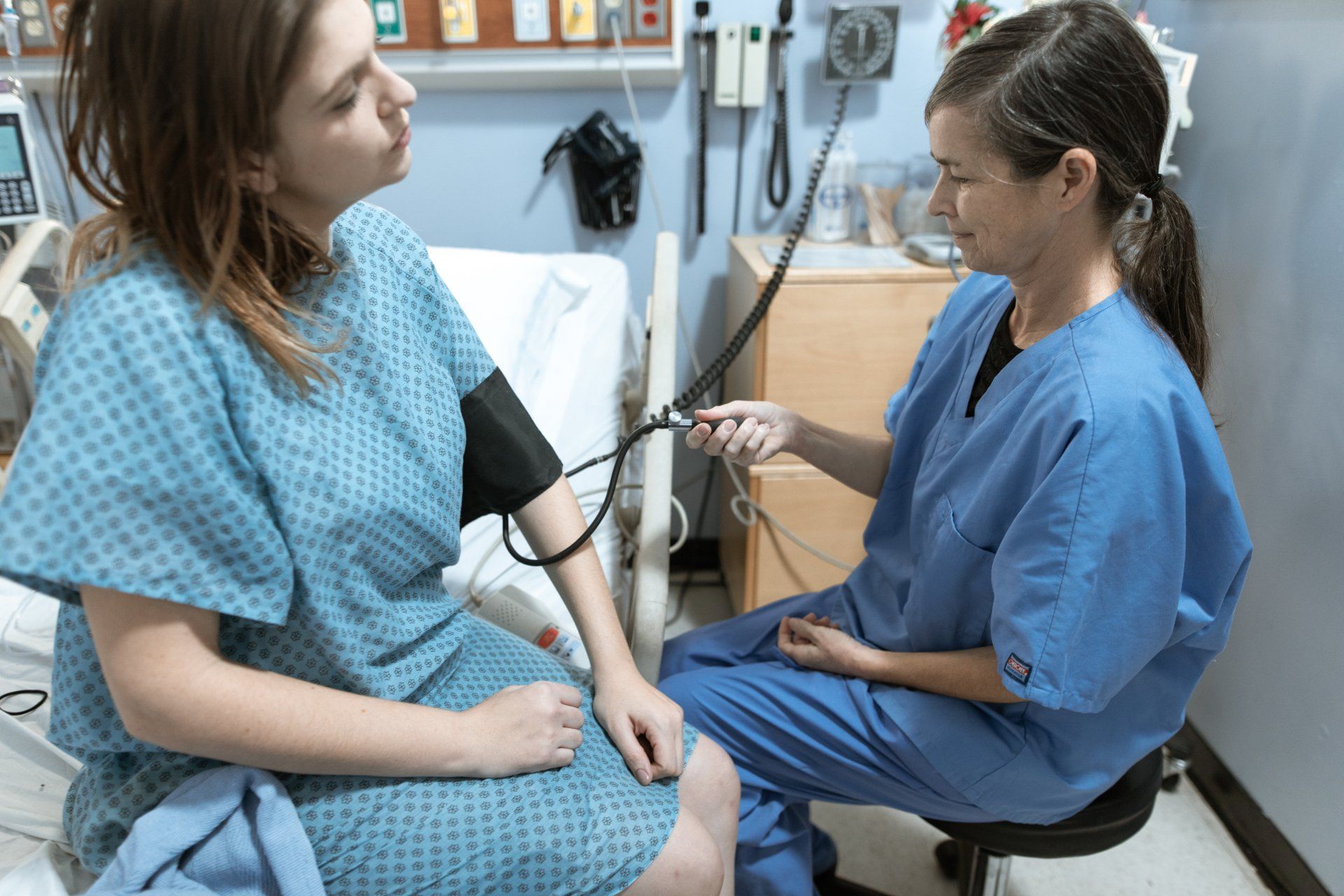
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against blood vessel walls. Simply put, it measures the pressure of the blood in your arteries as your heart beats and relaxes.
Blood pressure is measured with a sphygmomanometer and expressed with two numbers like a fraction. The unit for measurement is millimeters of mercury. The top number, the systolic pressure, is the blood pressure in your arteries when your heart beats or contracts. The bottom number, the diastolic pressure, is the blood pressure in your arteries when your heart relaxes between each beat.
The Role of Salt in the Body
One interesting thing about the human body is that it self-regulates.
One of the ways that the body does this is through homeostasis - the process through which it maintains stability while adjusting to optimal conditions, especially when the external environment changes. The kidneys play a significant role in homeostasis by maintaining fluid levels and electrolyte balance. The kidneys also help regulate blood pressure by secreting hormones that constrict or relax the vessels responsible for transporting blood.
Salt is essential to the normal function of our body. It assists with muscle function and nerve transmission. It contributes to homeostasis by maintaining fluid balance and supporting the operation of the kidneys.
The Connection Between Salt and the Development of High Blood Pressure
It is not news that too much salt consumption is detrimental to your health. Some research has shown there may be a solid connection between salt and the development of high blood pressure.
Too much salt can increase the sodium in your bloodstream and disrupt the body's electrolyte balance. High sodium levels cause your body to retain more water and fluid to dilute and reduce it. Higher fluid levels and water in the blood increase the pressure exerted against the blood vessels' walls, raising the blood pressure.
This sequence of events potentially leads to hypertension - high blood pressure.
Debunking the Myth: Does Salt Directly Cause High Blood Pressure?
Certain historical perceptions show that increased salt consumption would contribute to the subsequent increases in blood pressure. However, recent studies and publications have demonstrated that the relationship between both is less direct.
Medical News Today highlights a recent study submitted at Experimental Biology 2017 that shows a different view of the sodium-hypertension relationship. Lynn Moore from Boston University School of Medicine and her team studied data across 2,632 adults aged 30-64 from the Framingham Offspring Study. The research showed that those with lower sodium intake (less than 2,500 mg/day) had higher blood pressure than those who had consumed higher quantities of sodium over 16 years. The findings were contrary to the general assumption about sodium consumption. Instead, they aligned and added to recent studies that showed a "J-shaped relationship" between cardiovascular risk and sodium intake. The growth curve indicated an exponential growth of risk of cardiovascular diseases regardless of the level of salt intake.
Here is the implication - a level of salt intake such as the one suggested by the World Health Organization (<5 g per day) is equally dangerous as a level >12 g per day. It also indicates that the recommendation for sodium intake may need to be revised.
This study also highlighted the importance of high potassium consumption on blood pressure and other cardiovascular diseases. Individuals with the lowest blood pressure had the highest intake of potassium and sodium and vice-versa.
Given the limited effect of sodium consumption on high blood pressure, dietary recommendations and guidelines may change subsequently. Genetics, age, lifestyle choices, BMI, and underlying health conditions are contributing factors that must also be considered.
The Impact of Other Factors on Blood Pressure
The research above suggests that excessively low and high salt consumption harms your health. As a result, it is essential to note that increased salt consumption is not the only cause of elevated blood pressure levels.
Focusing solely on limiting salt intake is insufficient in managing blood pressure, as increased salt consumption causes elevated blood pressure levels. Other factors should be considered as well, including:
- Age
- Genetics
- Lifestyle choices
- Stress management
- Underlying health conditions
- Age and Genetics:
Research has shown that blood pressure tends to rise with age. Genetics and family history also greatly influence every individual's propensity to high blood pressure.
- Lifestyle choices:
Negative lifestyle changes, such as excessive alcohol intake and smoking, significantly elevate blood pressure.
Smoking constricts the blood vessels and increases heart rate. By raising blood pressure, the risk of potential heart failure increases.
Positive lifestyle choices like eating healthy and exercising can help lower blood pressure and improve an individual's overall health.
Potassium consumption also plays an essential role in regulating blood pressure. Hence, a well-rounded diet would include potassium-rich foods.
Long-term stress may contribute to sustained high blood pressure. Short and sustained blood pressure spikes can lead to heart attacks and strokes due to frequent dilation and constriction of blood vessels.
- Underlying Health Conditions:
Underlying health conditions like kidney diseases, diabetes, and hormonal disorders can impact blood pressure levels.
Alternative Seasonings and Flavor Enhancers to Replace Salt
Various herbs, spices, and flavorings are healthier alternatives to salt. Some of these include:
- Herbs: These can be in the fresh or dried form (basil, parsley, cilantro)
- Spices (cumin, turmeric, nutmeg)
- Aromatic vegetables (onions, ginger, garlic, Bell peppers)
Tips for Reducing Your Salt Consumption
Here are some tips to help reduce your salt intake:
- Lower your intake of packaged and processed frozen foods: Packaged foods such as meat, fruits, and vegetables usually contain added high-sodium seasonings and sauces used to preserve the foods. You can drain the brine (salty water) used to preserve canned foods and rinse the food thoroughly to remove excess salt. Incorporate fresh cuts of meat, fruits, and vegetables that do not contain sauces or seasonings in your diet.
- Cook more often: Cooking at home gives you control over the seasonings used in your meals. It would also help reduce the intake of restaurant foods, which usually contain high sodium levels. When you decide to dine out, research extensively.
- Use herbs and spices: Choose natural spices and herbs as an alternative to salt. These spices may be dried or fresh and add a lot of natural flavor to your meals.
- Read food labels: Food labels usually include the dietary content of each product on the Nutrition Information Panel. Compare the dietary value of similar products.
- Reduce the intake of sauces and packaged seasonings: Sauces used in making curry and dipping sauces usually contain significant amounts of salt. Ensure that you research well and take these sauces in minimal quantities, as some brands may have inscriptions that indicate they have "less salt or sodium" but are not "low in salt or sodium."
In conclusion, salt is not the only cause of high blood pressure. While salt intake reduction plays a significant role in a healthy lifestyle, it is only a small factor in managing blood pressure. Choosing a balanced approach to your nutrition and lifestyle would benefit blood pressure and overall health.
Always consult a health professional before making significant changes to your diet.
References
- How Salt Can Impact Your Blood Pressure, Heart, and Kidneys
- Common High Blood Pressure Myths | American Heart Association
- High blood pressure: Sodium may not be the culprit
- It's Time to End the War on Salt - Scientific American
- Salt Doesn't Cause High Blood Pressure?
- 5 Ways To Reduce Salt Intake - Heart Foundation
Thank you for reading Patient Education Essentials, the Write Shift RN blog.
Disclaimer: This article was written as a guest post for Write Shift RN LLC's blog. The information in it may not be wholly fact-checked or edited, allowing the reader to see the writer's work and skills firsthand. This information is not intended as medical advice. It is for informational and educational purposes only. Always talk to your doctor or other qualified healthcare providers about any questions or concerns you may have regarding medical conditions.











